Out of many different species of fungi, there are only a few that are responsible for human illness. A fungus does not belong to the family of bacteria or viruses, but still, it can cause an infection. Yeast is a fungus. Also, mushrooms and molds belong to the category of fungi. Yeast is often associated with the vagina and is one type of yeast infection. There are other types of yeast infection as well that can affect skin all over the body. It is important to know that we can’t see many types of fungi present on our skin and body. Most of the times these fungi don’t cause any problems, but sometimes, a fungus leads to an infection. This guide will help you know six more common fungal and yeast infections that people experience.
- Athlete’s foot- The most common fungal infection of the feet, Athlete’s foot is also known as tinea pedis. Different types of athlete’s infections are there but the most commonly reported in between the toes. This fungal infection leads to intense itching episodes and breaks down the skin of the feet with redness and scaling. The infection can be treated with topical treatments like creams or lotions, and severe cases of Athlete’s foot require an oral antifungal medication to get rid of the infection.
- Tinea versicolor- Also called pityriasis, Tinea Versicolor is a fungal infection of the epidermis (the top layer of the skin). The yeast responsible for causing this infection lives on oil glands, so teens and young adults tend to get the rashes caused by pityriasis versicolor as compared to older people. A variety of treatment options are available for treating the infection, but they often come back. Fortunately, an individual having this infection doesn’t show any signs of pain or itching.
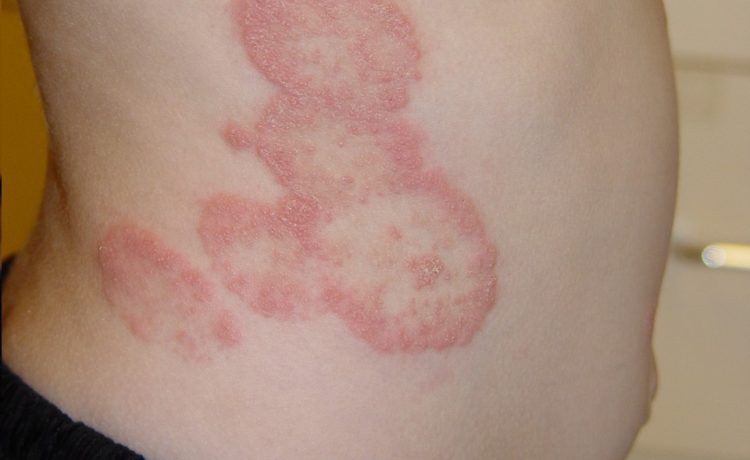
- Ringworm-The common fungal infection of the skin also known as tinea corporis. Several fungi that live in the epidermis could lead to ringworm infection. This fungal infection tends to cause more symptoms than tinea versicolor, and it appears in the form of a red or silver noticeable rash anywhere on the body. The rash usually appeared as ring-shaped and consisted of red, scaly patches, or bumps. The ring-shaped rash makes for an easy diagnosis. It can be treated easily with an antifungal cream.
- Ringworm of the scalp – A more intensive fungal infection, Ringworm of the scalp is also called tinea capitis and is ringworm that affects the scalp. The fungal infection is more common in children. It does not only invade the skin of the scalp but also hair follicles. Infected hair can often fall or break leaving a bald area with a ringworm type rash in the center. The condition doesn’t improve well with topical creams so it should be treated with oral antifungal medications.
- Fungal nail infection- Commonly known as onychomycosis, fungal nail infection is caused due to a fungal infection of the toenails or fingernails. During the condition, a nail grows, it becomes brittles, thickens, and get separated from the nail bed which can cause pain and discomfort. Nail infections caused by fungus should be well treated with oral antifungal medications because topical treatments don’t help with the nail infection. Nail infection is caused by dermatophytes which require keratin for nutrition.
- Cutaneous candidiasis- Another type of fungal infection that involves any skin is of the body, but mostly affect areas like armpits and groin. Candida is the primary cause of nappy rash in infants. It is also common in people who have diabetes and are obese. Most dermatologists recommend steroid therapy for treating the infection.
What causes Fungal Infections?
Invasive fungal diseases are rare in healthy individuals because of a sophisticated immune system. However severe fungal infections majorly attack immunocompromised people. Uncontrolled HIV and cancer treatments such as chemotherapy make many people vulnerable to lethal fungal disease. Diabetes can also compromise our immunity. Also, immunosuppressants, corticosteroids, and long-term use of antibiotics can make you prone to get a fungal infection.
Investing Fungal Infections
A fungal infection can be diagnosed by clinical appearance alone, but in some cases, laboratory examination of skin scrapings, nail cutting can help when the diagnosis is uncertain.