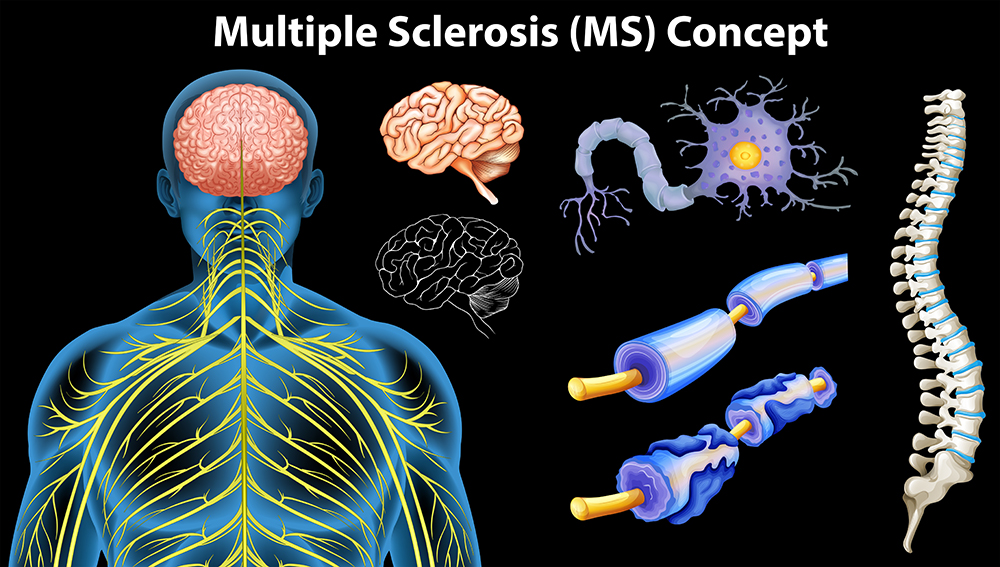
People suffering from multiple sclerosis (MS) are more likely to have problems with their respiratory tract. They may also experience symptoms like fatigue, tingling, numbness, and the memory problems. It has been estimated that about 30% of MS patients have decreased respiratory function. If you have MS, there are chances that you got fewer points on pulmonary function tests that assess the muscle strength when you breathe.
A decrease in your ability to breath properly and to cough effectively enough to clear out secretions or food from your airways in the lungs has also been reported. These changes in your respiratory tract may cause pneumonia (respiratory infection).
Also Read: Immunosuppression, Immunodeficiency Disorders, and Possible Remedies
MS related respiratory problems
Patients who have MS tend to have shallower and faster breathing than those who don’t have. This condition is the base of most MS associated problems which includes:
- Trouble breathing deeply
- Shortness of breath
- Cough
- Not enough air
- Hiccups
- Frequent sighing
If you have experienced any of these breathing issues due to MS, it may make you feel uneasy and as if you:
- Are trying to breathe with a blanket over your head
- Are not able to take a deep breath
- Have a heavy weight on your chest area
Effect of MS on lungs
There are numerous ways that MS can result in breathing problems, including the following:
- Muscle weakness and spasticity –Breathing can be affected by weakness. When the muscles in your respiratory tract that help with inhaling and exhaling are weak, you may experience difficulty breathing; you may find yourself unable to breathe deeply to bring in the oxygen you require. Spasticity in respiratory tract muscles contributes to the problem.
- Aspiration pneumonia- MS associated swallowing problems or inability to clear mucus from the nose or throat may result in aspiration pneumonia, which can occur when food or drink can be inhaled into the lungs.
- Sensory problems- MS related breathing difficulties may cause due to abnormal respiratory sensory information involving:
- Abnormal pressure in the lungs
- Motion of the lungs and chest wall
- Airflow
- Multiple sclerosis medications– Some medications prescribed to get rid of pain and spasticity associated with MS can cause side effects like slower, shallower breathing. These medications include tranquilizers, opioid-based pain medication, and muscle relaxants.
In rare cases, MS associated breathing problems become life-threatening or so severe that a patient requires breathing tubes or supplemental oxygen. However, mild breathing issues can lead to fatigues. Additionally, the feeling of not getting enough oxygen can result into severe anxiety and panic attacks.
Seek Medical Help
The good news is that a treatment called respiratory therapy is available to help MS patients with breathing problems. This may include breathing exercises to improve overall function and prevent respiratory tract problems during later stages of MS. The therapy is very effective in helping MS patients to breathe normally.
Tips to improve your breathing
The following are the tips for improving your breathing:
- Minimize your risk of getting a respiratory infection by avoiding contact with sick people. Wash your hands before eating food or snacks. Get your flu shot and get enough rest to keep your immune system strong. If you start feeling sick or develop a cough, immediately seek medical attention.
- Do not talk or laugh while eating food. Always chew your food carefully to help prevent coughing and choking.
Also Read: How to get longer Eyelashes with Careprost
If you visit your health care specialist for regular check-ups, tell him/her if you have reduced lung function from MS. This will help your health care provider in determining the best treatment.