The treatment of hair loss diseases is quite difficult because of insufficient efficacy and limited options. However, recent technologies have developed to improve the treatment of refractory hair loss conditions.
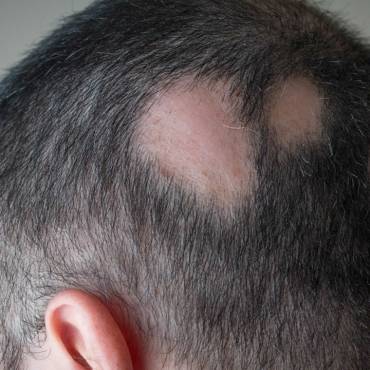
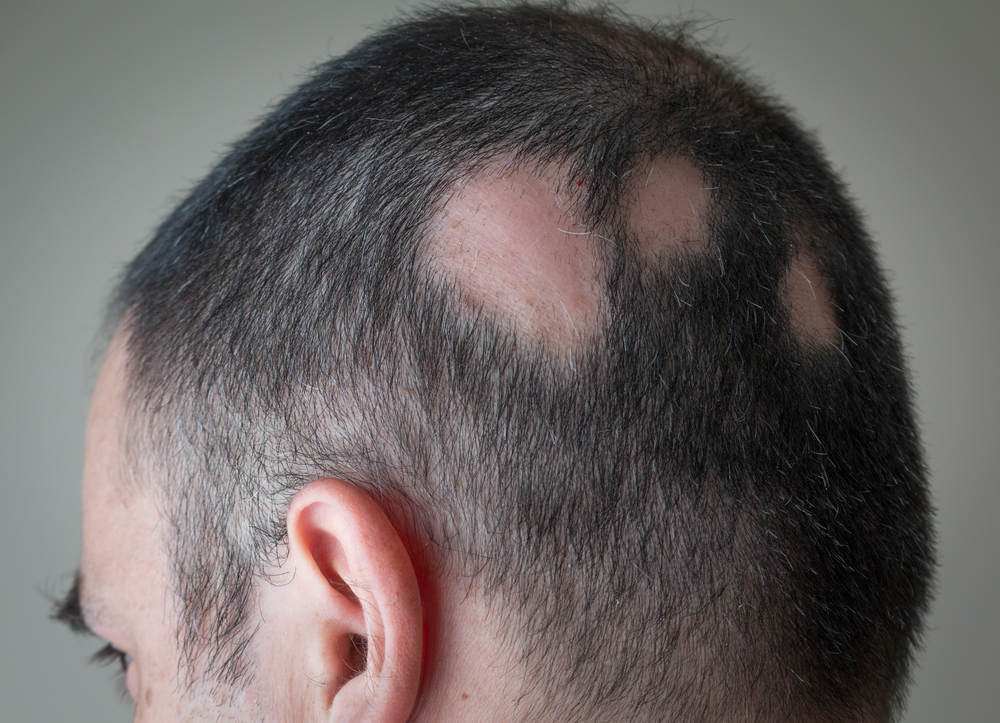
Alopecia areata is a common non-scarring alopecia that can develop at any age. It has been estimated to affect around 0.1% to 0.2% of the people and accounts for 0.7% to 3% of all cases. It can be identified as an anti-inflammatory disease that manifests in the hair follicles and can also affect the nails up to 66% of patients with hair loss condition. Alopecia areata develops irrespective of race and gender. However, it is thought that it is prevalent in the male adult population. The condition is highly prevalent between the ages of twenty to forty years of life. However, according to research, 60% of alopecia areata sufferers will present with their first bad patch in their teenage.
Also Read: Beneficial tips to get healthy hair
Alopecia areata is responsible for causing small round patches of baldness, especially on the scalp. Although, the baldness patches can also appear on eyebrows, beard, and eyelashes. In some case, the condition covers a large area and rarely it covers the whole scalp or even the entire body and scalp. You cannot predict how much hair you will be going to lose. Regrowth is possible over a period of months, or in some cases, it takes years to grow back, but the re-growth cannot be guaranteed. The chance of regrowth is more when the hair loss is less or at the beginning stage. A majority of people with a few small bald patches get full re-growth within a year. If you have almost lost half of hair, then the chances of full recovery are very less.
Causes of alopecia areata
Hair loss occurs because the hair is affected by inflammation. However the cause of inflammation is still not known, but it is believed that the body own defence system (immune system) that usually protects the body against infections and others health issues, may attack the growing hair. The reason behind this action is still not understood.
Alopecia areata is not contagious, and there is no link between food or vitamin deficiencies. Stress rarely appears to trigger the condition. It is estimated that there is about 20% of people with alopecia areata that have a family background of the disease.
Symptoms of alopecia areata
An individual suffering from alopecia areata may experience a tingling sensation in the scalp; the condition can upset you as the bald area cannot be disguised by hairstyle.
If you have a patch on your eyelashes then this may become sore due to dust particles, particularly in the wind.
Treatment of alopecia areata
People with the mild condition does not require treatment as the chances fo hair growth is high without the treatment. Some treatments are available that help induces hair growth though none can alter the overall course of the hair loss condition.
The hair loss treatments may include:
- Steroid Creams- These creams are meant to be applied on bald patches twice daily for a restricted time.
- Local steroid injections-These injections are injected directly into the scalp and eyebrows. The treatment is one of the most effective approaches for small bald patches. Injections can be injected every four to six week by a dermatologist. The hair loss treatment should be stopped once regrowth is achieved. You may develop a small simple at the injection site which is not the thing to worry as this disappears with time. Caution should be exercised while injection into eyebrows as excess medication can result in glaucoma (an eye condition defined by a raised pressure in the eyeballs).
Also Read: Ultimate tips for common skin and hair problems
- Steroid tablets-large dose of steroid tablets are given for regrowth of hair. The treatment is not as effective as injections as there are chances of recurrence of disease after stopping the treatment.