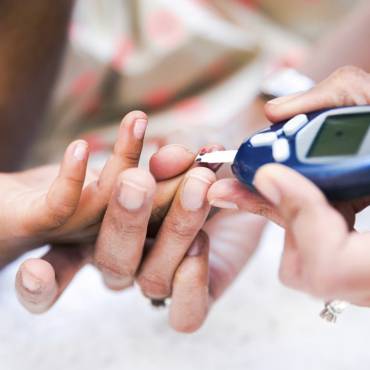
Medications, including insulin, are prescribed to people with type 2 diabetes to help control their blood sugar levels. Most of these anti-diabetics are available in tablet form for oral administration, but some are administered intravenously as injections. These pills and injections are intended to be used in combination with regular physical activity and healthy eating (not as a substitute).
These anti-diabetic pills are not an oral form of insulin. With recent drug development in the field of diabetes, not all injectable drugs are insulin. These type 2 diabetes medicines may cause adverse effects. Talk to your healthcare provider if you experience any problems while taking anti-diabetic agents. An alternative medication is usually available for patients who experience side effects from an anti-diabetic agent.
Types of type 2 diabetes medications to manage the condition
Currently, there are six classes of pills used for controlling blood sugar levels and two classes of injections. The pills are known as sulphonylureas, glitazones, alpha-glucosidase inhibitors, biguanides, DPP-4 inhibitors, and meglitinides. On the other hand, the two categories of medications given intravenously are incretin mimetics and insulin. These are typically considered one of the best medicine for type 2 diabetes by doctors. Let’s read them in detail:
Biguanides (metformin)
These medicines help to control high blood sugar levels by decreasing the amount of stored glucose released by the liver. It slows down glucose absorption from the intestine and helps your body become more sensitive to insulin, allowing your insulin to work more effectively.
This tablet should be taken before or after meals to avoid gastrointestinal problems. The dose of biguanides should be started at a low dose and increased gradually. The medications of this category have been shown to improve the overall health of patients with type 2 diabetes. That’s why metformin is often considered to be the first choice in controlling blood glucose levels in patients with type 2 diabetes.
The adverse effects of the medicine include diarrhea, a metallic taste in the mouth, and nausea.
Sulphonylureas
These medications work to stimulate the pancreas to release more insulin in patients with type 2 diabetes. They can cause hypoglycemia. Make sure to discuss the problem with a healthcare provider. These pills must be taken on an empty stomach (just before a meal). There is a reduced risk of hypoglycemia if you have regular meals throughout the day. Considering the progressive nature of type 2 diabetes, your health care specialist may gradually increase the dose over time. Sulphonylureas may be given in combination with metformin pills.
This class of medicine can cause side effects such as stomach problems, jaundice, and skin rashes (rare).

Meglitinides
These medications are known to lower blood glucose levels by stimulating the pancreas to release more insulin; however, they are not chemically associated with the sulfonylurea class of medications. They are called fast-acting medications and don’t last long, so a pill is taken before each meal to stimulate insulin and help manage the meal. The uses of these drugs are contraindicated in pregnant and breastfeeding women.
They can cause a deficiency of glucose in the bloodstream (hypoglycemia). Discuss hypoglycemia with your healthcare provider, and your healthcare specialist will offer you an alternative to cope with the situation. Gastrointestinal problems and abnormalities of liver function tests are the side effects of Meglitinides.
Thiazolidinediones (Glitazones)
Glitazones help to control diabetes by increasing the effect of your insulin, particularly in muscle and fat cells. The effect is slow; these medications may take days to a week to start working and one to two months for complete results. Glitazones work effectively in combination with other diabetes medications.
The use of this medicine is contraindicated in women who are pregnant and lactating. While taking these tablets, it is recommended to visit your healthcare specialist for regular liver function tests during the first year of diabetes treatment.
This medicine causes unwanted weight gain. Engage in exercise to shed unwanted weight. Another adverse effect of using thiazolidinediones, such as Glitazones, is fluid accumulation. People with heart failure should avoid these medications, and it is also not recommended in case of liver problems.
For complete diabetes care, take the correct dose at the right time, exactly as prescribed by your health care specialist.
Other categories of medications: Incretin mimetics and insulin
Incretin mimetics – also referred to as GLP-1 receptor agonists. It belongs to the class of drugs used to treat type 2 diabetes. This medicine mimics the action of incretin hormones, which stimulate the release of insulin in response to food intake. Incretin mimetics help lower blood glucose levels in the body by increasing insulin production, slowing stomach emptying, reducing glucagon secretion, and promoting a feeling of fullness.
Insulin injections – This method delivers insulin (a hormone that helps regulate blood sugar in the body). This is usually prescribed when your sugar levels are not controlled with diabetes medicines.
Consult your doctor to determine the best diabetes treatment and medication that suits your needs.