As a diabetic patient, your everyday routine involves scheduling and planning. Stress in an emergency or a natural disaster can increase or decrease the blood sugar level to a dangerous level. It may be difficult to handle the situation. There may be no food or diabetes medication available at that particular near around you, and no way of getting medical attention.
An emergency diabetes kit can help you to self-control your blood glucose levels, during and in an emergency. With the help of diabetes kit, one can reduce the risk of diabetes-related infections and life-threatening conditions. Keep the diabetes care kit in a safe place and keep it up to date to avoid any health complications.
Also Read: How Can You Beat Your Diabetes?
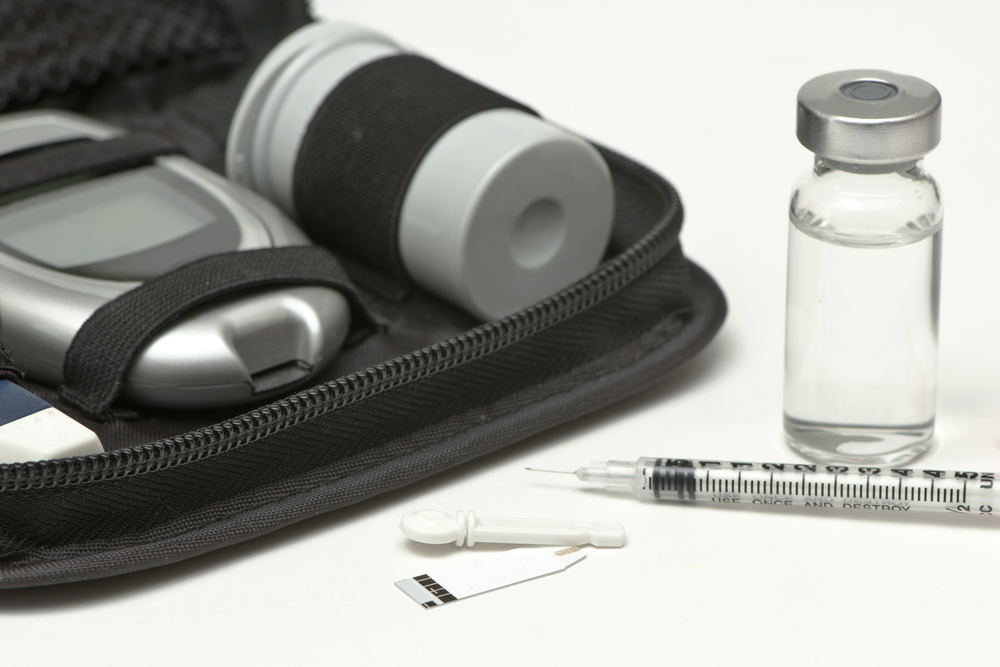
Diabetes Kit Checklist
- A copy of your diabetes medication regimen provided by your health care specialist
- Copy of emergency information and medical list
- A list of medical history
- Syringes
- Cotton balls and tissues
- Insulin or pills, including all your prescribed blood pressure medications and diabetes medications
- Alcohol swabs
- Blood glucose diary
- An instrument to measure blood glucose levels
- Insulin pump supplies (if told to use insulin pump)
- Strips for your meter
- Glucagon emergency kit (if on insulin)
- Urine ketone testing strips
- Lancing device and lancets
- Longer lasting carbohydrate sources such as cheese and crackers
- Quick acting carbohydrate sources like glucose tablets and orange juice
Useful tips about insulin, syringes, and pens
- Insulin should be stored at room temperature for 28 days.
- Insulin should not be exposed to excessive cold, light, and heat.
- Lantus insulin should be cleared on a regular basis.
- Insulin that sticks to the side of the bottle should not be used.
- Insulin pens can be stored at controlled room temperature according to manufacturer’s directions.
- Reuse of insulin syringes is not recommended. Do not share your insulin syringes with other people.
Important things to remember during Diabetes Treatment
- Stress can raise or lower your blood glucose level.
- Irregular intake of meals can cause changes in your blood sugar levels.
- Avoid doing the excessive workout when your sugar level is over 250 mg as it can cause your blood sugar to go high.
- Always wear protective clothing and sturdy shoes
- Check your feet regularly for irritation, blisters, open sores, and infection. An emergency or a natural disaster can increase your risk of injury. Inability to change footwear, excessive dampness, cold, and heat can cause an infection, especially when your blood glucose levels are high. Avoid stepping out without wearing shoes.
Helpful tips for a hot weather
- Avoid doing workouts outside.
- Try to wear light-colored cotton clothes.
- Stay inside in the air conditioned atmosphere or fan cooling comfort, according to your body requirement.
- Do not take salt tablets unless prescribed by your health care specialist.
- Drink plenty of water to keep yourself hydrated. (Drink at least 8 glasses of water a day)
- Seek immediate medical help if you experience fever, abdominal cramps, fatigue, confusion, weakness, and decreased urination.
Food items to be stored for Diabetes Care
- One jar peanut butter
- One small box powdered milk
- Two packets of cheese and crackers
- One packet of dry, unsweetened cereal
- Canned orange or apple juice
- Four packets of glucose tablets
- Few hard candies for low blood sugar
- Cans of diet soda and regular soda
- Water
- Disposable cups
- Mechanical can opener
- Spoon and knife
Food consideration during an emergency
- Drink lots of water daily
- Avoid eating contaminated food
- Maintain a meal plan to be the best of your availability
- Limit sugar containing food such as frosted cake, honey, jellies, gelatin, cookies, chocolate, pastry, custards, pre-sweetened or sugarcoated cereals, ice cream, etc.
- Regularly check your blood glucose levels and note down in a diary.
- Don’t eat greasy or fried food.
- Limit products with sugar-containing ingredients like sucrose, fruit syrup, corn syrup, honey, brown sugar, dextrose, sugar, molasses, etc.
- Increase your food and water intake during periods of physical activity; you can eat between meal snacks before physical activity or can eat additional food with meals.
- Eat your meals and snacks daily at the same time. Never left yourself hungry. The frequency and quantity of your food intake should remain same day to day depending upon your level of physical activity.
- Always carry a fast source of sugar with you. A source of sugar may include three glucose tablets, one small box of raisins, or some hard sugar candies.
Also Read: Diagnosing Breast Cancer
Extra Medication
For type 2 diabetes treatment, pills are required to help your body use insulin better. People with type 1 diabetes and some with type 2 diabetes required to keep a supply of insulin, insulin pens, and syringes in the diabetes care kit.



