Although, Parkinson’s disease is non-curable, getting the hang of the disease will make you go through less suffering. Read below to learn Parkinson’s disease symptoms and treatments.
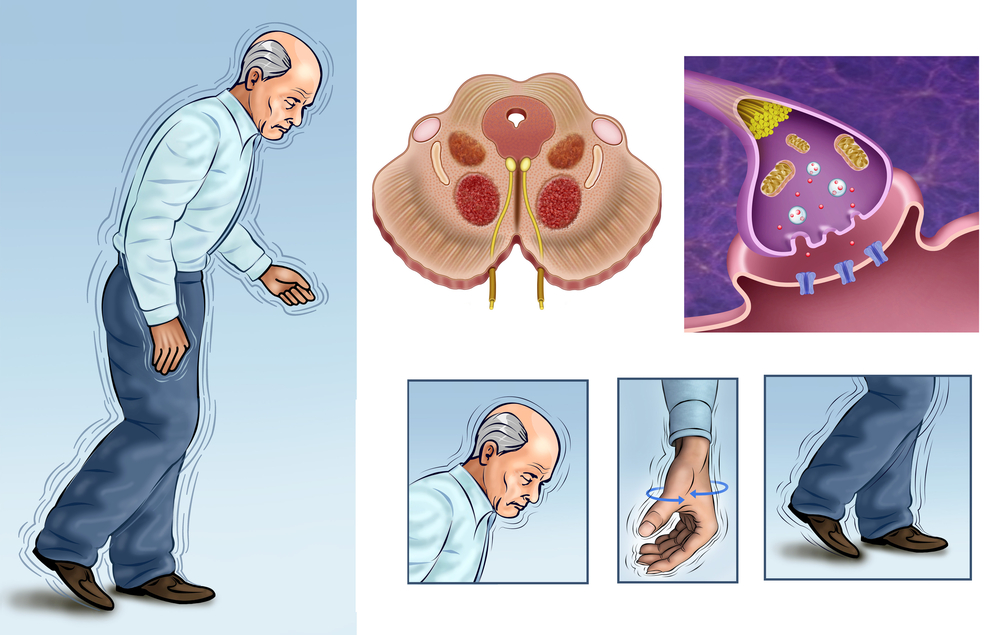
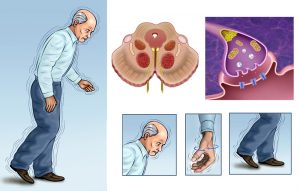
Parkinson’s disease affects the nervous system and has a direct impact on the movement of the body parts. It is a progressive disorder that develops over time. Sometimes it starts with a not so noticeable tremor in just one hand. However, just a tremor may be the most eminent sign of the disease leading to further slowing or stiffness of movement.
In the early stages of the disease, your face may reveal little or no expression, or the movement of your arms may get restricted while you walk. Your voice may become soft or inaudible. Parkinson’s disease symptoms go downhill as your condition advances over time.
Parkinson’s disease symptoms may include:
Tremor: A tremor or shaking usually begins in a limb, often your hand or fingers at the state of rest.
Bradykinesia or slowed movement: With progression of the disease, your ability to move may get reduced which would make simple tasks difficult and time-consuming. You may take shorter steps while walking, or you may find it difficult to get out of a chair.
Rigid muscles: Your muscles stiffen thereby, limiting your range of motion and causing pain.
Impaired posture and balance: Your posture may become bent, or you may have problem in maintaining your body balance.
Loss of automatic movements: Your ability to perform unconscious movements such as smiling, blinking, or swinging your arms when you walk may weaken with progression of the disease.
Speech changes: Your speech may become soft, quick or slurred.
Writing changes: The simple task of writing may turn out to be a big deal and your writing may appear small.
Also Read: How to identify Parkinson’s disease symptoms
Parkinson’s disease treatments:
Parkinson’s disease can’t be cured but its symptoms can be controlled by undergoing medication based treatment. In some advanced cases, surgery may be recommended.
Medications:
Medications may be helpful in the management of problems with walking, movement and tremor. These medications function by increasing or substituting dopamine, a signaling chemical present in the brain whose deficiency causes the disease.
Some of the medications that your doctor may prescribe include:
• Carbidopa-levodopa- Levodopa is a chemical that passes into your brain and gets converted to dopamine. It is the most effective medication for Parkinson’s disease cure. For making most of this medication, it is given in combination with carbidopa. This combination drug includes Rytary and Sinemet.
• Dopamine agonists- They are similar in action to dopamine and work by mimicking the effects of dopamine in the brain. These drugs have a long-lasting effect than Levodopa and may be given with levodopa to manage the off-and-on effect of levodopa.
Dopamine agonists include ropinirole, pramipexole, rotigotine (given as a patch) and, apomorphine.
• MAO-B inhibitors- These medications include selegiline and rasagiline. They prevent the breakdown of dopamine in the brain by inhibiting monoamine oxidase B (MAO-B), a brain enzyme which breaks down brain dopamine.
• Tolcapone (Tasmar)- It works by inhibiting an enzyme called COMT inhibitor. This medication is rarely used as it has a potential to cause serious liver damage and failure.
• Anticholinergics- These medications include benztropine or trihexyphenidyl. They are effective in controlling the tremors associated with Parkinson’s disease.
• Amantadine- Amantadine provide short-term relief of symptoms of mild, early-stage Parkinson’s disease. It may also be given with carbidopa-levodopa therapy during the later stages of Parkinson’s disease to control involuntary movements (dyskinesias) induced by carbidopa-levodopa.
Surgical procedures:
Deep brain stimulation or DBS is a surgical procedure wherein a surgeon places electrodes into a specific part of patient’s brain. The electrodes are connected to a generator implanted in the chest near the collarbone that sends electrical pulses to the brain and may reduce Parkinson’s disease symptoms.
Also Read: Foods to avoid when diabetic
DBS surgery has it’s own risks including infections, stroke or brain hemorrhage. Some people experience problems with the DBS system or have complications due to stimulation, and they may need adjustments or replacements in some parts of the system.
Deep brain stimulation is mostly recommended to people in whom Parkinson’s disease reaches the advanced stage. DBS can stabilize medication fluctuations, reduce or halt involuntary movements (dyskinesias), reduce tremor, reduce rigidity, and improve slowing of movement.
DBS is effective in controlling erratic and fluctuating responses to levodopa or for controlling dyskinesias that don’t improve with medication adjustments.
Although DBS may provide sustained benefit for Parkinson’s symptoms, it doesn’t keep Parkinson’s disease from progressing.