Skin bleaching refers to using products that help lighten the dark skin areas or achieve a lighter complexion. Skin bleaching products include bleaching creams, gels, soaps, tablets, and professional treatments like laser therapy and chemical peels.
Marketing companies allure users by giving fancy dreams with costly marketing tricks, stating their products as skin whitening cream, quick whitening cream, instant lightening cream, day brightening cream, etc. Choosing the right product is crucial to achieve the desired results. A consultation with a dermatologist is a good way to use skin cream or products. The second option is to review users’ feedback about the product in detail to understand if the product is really good.
Results from skin bleaching agents aren’t guaranteed, and research shows that skin lightening products can cause skin complications and side effects. Medical experts suggest no need to lighten the skin, but if you still like to consider it, understand the associated risks.
Skin bleaching is generally sought for specific cosmetic or medical reasons, including:
-
- Hyperpigmentation – Conditions like melasma, sunspots, or post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation can lead to uneven skin tone.
- Dark spots – Age spots or dark patches can be lightened to achieve a more uniform complexion.
- Acne scars – Some individuals may use bleaching products to reduce the appearance of dark marks left by acne.
- Skin conditions – Certain dermatological issues may lead to pigmentation changes that some may want to address.
- Cultural or personal preference: In some cultures, lighter skin is preferred, which can drive individuals to seek skin-lightening products.
Approach skin bleaching cautiously, considering the potential risks and side effects. Consult a dermatologist first to discuss potential risks and safe alternatives. Skin bleaching products often contain ingredients like hydroquinone, kojic acid, or corticosteroids. However, these products can have side effects, including skin irritation, increased sensitivity, and, in some cases, more severe conditions like ochronosis or increased risk of skin cancer.
The safety of skin bleaching creams can vary significantly based on their ingredients and how they are used. Here are some important points to consider:
-
- Active ingredients: Some common ingredients, like hydroquinone, can be effective but may cause side effects such as irritation, redness, and, in some cases, a condition called ochronosis (a bluish-black discoloration of the skin) with prolonged use.
- Regulation: In some countries, certain ingredients in skin bleaching products are banned or restricted due to safety concerns. It’s important to check the regulations in your area.
- Long-term use: Prolonged use of skin bleaching products can lead to skin thinning and increased sensitivity to sunlight.
- Consultation: It’s always best to consult a dermatologist before starting skin bleaching treatment. They can recommend safe and effective options tailored to your skin type and concerns.
- Alternatives: There are safer alternatives, such as chemical peels, laser treatments, and topical agents that can lighten skin without the risks associated with traditional bleaching creams.
While some products may be safe when used correctly and under professional guidance, many carry risks that should not be overlooked.
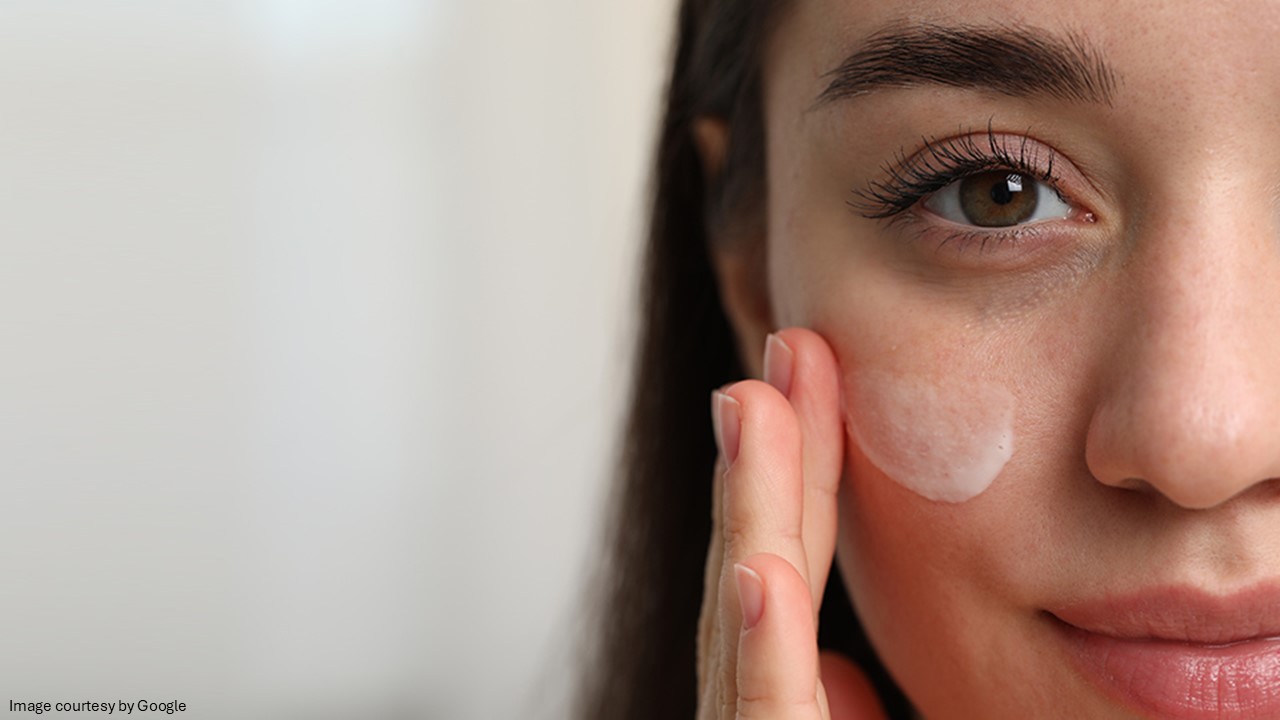

Hydroquinone
Hydroquinone is a skin-lightening agent commonly used to treat hyperpigmentation, dark spots, and melasma. Hydroquinone works by inhibiting the enzyme tyrosinase, which plays a key role in producing melanin, the pigment responsible for skin color. By reducing melanin production, hydroquinone helps lighten dark spots and areas of hyperpigmentation. It’s primarily used for conditions like age spots, freckles, and melasma. Hydroquinone products are used to treat:
-
- Melasma: A common skin condition causing brown to gray-brown patches, often triggered by hormonal changes.
- Post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation: Dark spots that remain after acne or other skin injuries.
- Age spots and freckles: Areas of hyperpigmentation that develop with sun exposure or aging.
Hydroquinone skin bleaching creams and other products are available in over-the-counter formulations (typically at lower concentrations) and prescription forms (higher concentrations).
Safety and Precautions
– Hydroquinone is banned or restricted in some countries due to safety concerns.
– Hydroquinone bleaching creams are generally recommended for short-term use, and a dermatologist should monitor long-term usage.
– It can increase sensitivity to sunlight. Use a broad-spectrum sunscreen with a high SPF while using the product.
– Individuals with certain skin conditions (e.g., eczema or sensitive skin) should avoid hydroquinone unless advised by a dermatologist.
– Hydroquinone before and after – Use the products as directed, and be cautious about combining them with other skin treatments.
Conclusion
While hydroquinone can be effective for treating hyperpigmentation, it’s essential to use it under the guidance of a dermatologist due to potential side effects and risks. Regular monitoring and following recommended usage guidelines can help minimize adverse effects while achieving desired results. Don’t hesitate to ask your dermatologist about other skin brightening creams or skin lightening products you may wish to use.
admin
Latest posts by admin (see all)
- What is Triluma Cream? Uses, Benefits, and How It Works for Skin - December 26, 2024
- What Causes Dark Spots? Understanding the Science of Hyperpigmentation and How Skin Lightening Products Help - December 26, 2024
- Tretinoin Gel vs. Cream: Which Formulation is Right for Your Skin? - December 20, 2024