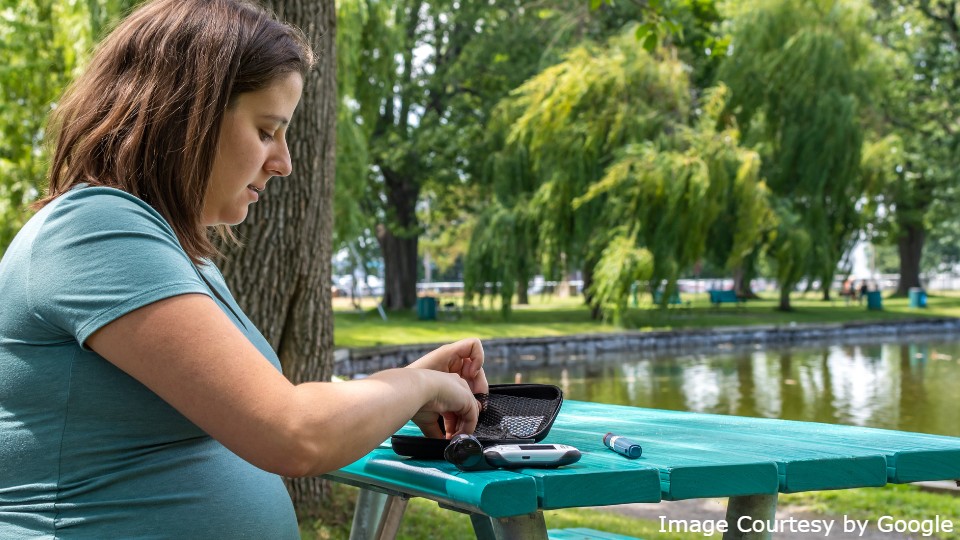
Diabetes is a group of metabolic disorders characterized by high blood sugar levels. Diabetes management requires a comprehensive approach, including medications, lifestyle changes, and regular monitoring to prevent complications and ensure optimal health outcomes.
Let’s understand the type of diabetes.
Types of diabetes:
-
- Type 1 diabetes – Autoimmune disease where the body attacks insulin-producing beta cells.
- Type 2 diabetes – Metabolic disorder where the body becomes insulin resistant.
- Gestational diabetes – This develops during pregnancy due to hormonal changes.
- Latent autoimmune diabetes in adults – Slow-progressing autoimmune disease.
- Maturity-onset diabetes in young – Genetic disorders affecting insulin production.
This page will focus on type 1 diabetes symptoms for women and how to manage them.
Type 1 diabetes is experienced when the body cannot produce enough insulin, a hormone that regulates blood sugar levels. It is a chronic autoimmune disease; it affects when the body’s immune system attacks and destroys the insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas.
The key causes of type 1 diabetes:
Diabetes symptoms women vary on several factors, and these include age, weight, existing disease, and heredity. The symptoms of type 2 diabetes in women may differ with type 1 diabetes.
Type 1 diabetes in women has distinct characteristics and considerations. It requires careful consideration because women’s health is more complicated than men’s. Here are some key causes of type 1 diabetes:
-
- Autoimmune Response: The immune system erroneously targets and destroys pancreatic beta cells.
- Genetics: A family history and genetic factors contribute to risk.
- Environmental Factors: Elements like viral infections and vitamin D deficiency may play a role.
- Hormonal Fluctuations: Events such as menstruation, pregnancy, and menopause can influence blood sugar levels and insulin sensitivity.
- Reproductive Health: Type 1 diabetes can affect menstrual cycles, fertility, and pregnancy outcomes.
- Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS): Women with type 1 diabetes have an increased risk of developing PCOS.
- Eating Disorders: Women may be more susceptible to eating disorders, including disordered eating and insulin omission.
- Mental Health: Conditions such as anxiety, depression, and stress related to the disease are common.
Type 1 diabetes symptoms in women
Some common symptoms that can be noticed are:
-
- Increased thirst and urination
- Fatigue
- Blurred vision
- Slow healing of cuts and wounds
- Frequent infections
- Unexplained weight loss
- Irregular menstrual cycles (in premenopausal women)
- Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) symptoms (in some women)
Special care:
Pregnancy:
Type 1 diabetes in pregnancy requires careful management to ensure the health and well-being of both the mother and the baby.
-
- Preconception planning: Optimize blood sugar control and adjust insulin doses before pregnancy.
- Pregnancy complications: Type 1 diabetes increases the risk of pregnancy complications, such as preeclampsia and preterm labor.
- Fetal risks: High blood sugar levels can increase the risk of fetal malformations and stillbirth.
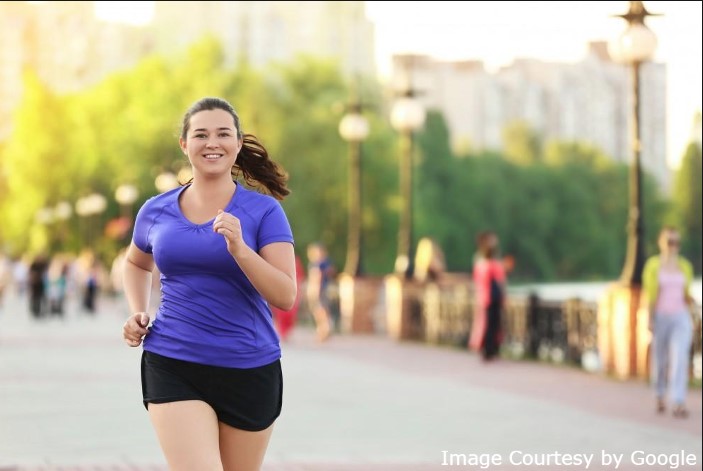

Menopause:
-
- Hormonal changes: Menopause can affect blood sugar levels and insulin sensitivity.
- Increased risk of complications: Menopause increases the risk of T1D-related complications, such as cardiovascular disease.
The management strategies for diabetic symptoms in women:
-
- Self-care – Develop a personalized treatment plan with a healthcare provider.
- Blood glucose monitoring – Regularly monitor blood sugar levels to adjust insulin doses and prevent complications.
- Insulin pump therapy – Consider using an insulin pump for more flexible and accurate delivery.
- Carbohydrate counting – Track carbohydrate intake to maintain stable blood sugar levels.
- Physical workout – Regular exercise and walking help control your blood sugar levels.
- Stress management – Yoga, deep breathing, and meditation are beneficial practices and techniques that help reduce stress.
- Menstrual cycle management – Speak to your doctor to adjust your diabetes medicine or insulin doses during your menstrual cycle.
- Pregnancy planning – Inform your doctor if you are planning a pregnancy to review blood sugar level medicine or insulin doses.
- Support network – Build a support network of family, friends, and healthcare providers.
- Stay updated – Keep an eye on the latest prevention, technologies, and management plans to avoid critical symptoms of diabetes in women.
Additional considerations:
-
- Reproductive health – Type 1 diabetes can affect reproductive health; work with your healthcare provider to address concerns.
- Eating disorders – Women with type 1 diabetes are at higher risk of developing eating disorders; seek help if needed.
- Mental health – diabetes can also impact mental health; prioritize self-care and seek help when needed.
Understanding the right aspects of diabetes in women and implementing effective management strategies can diminish the effects. The right care can lead to healthy and happy living.
admin
Latest posts by admin (see all)
- What is Triluma Cream? Uses, Benefits, and How It Works for Skin - December 26, 2024
- What Causes Dark Spots? Understanding the Science of Hyperpigmentation and How Skin Lightening Products Help - December 26, 2024
- Tretinoin Gel vs. Cream: Which Formulation is Right for Your Skin? - December 20, 2024